Desserts
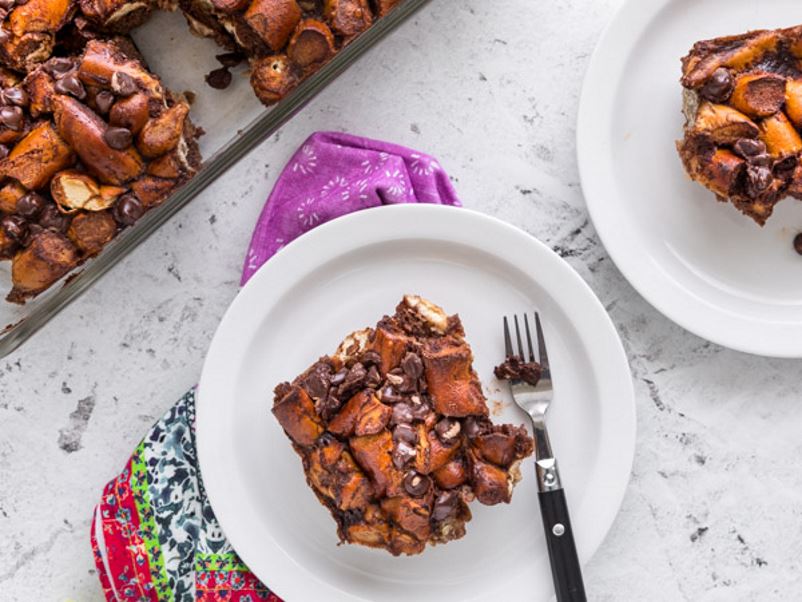
Philly Soft Pretzel Bread Pudding with Chocolate Recipe
What's better than healthy comfort food? This recipe uses Philadelphia-style soft pretzels for a unique twist on bread pudding.
See More